|
TERM |
DEFINITION |
CHARACTERIZATION |
ACTIVITY |
|
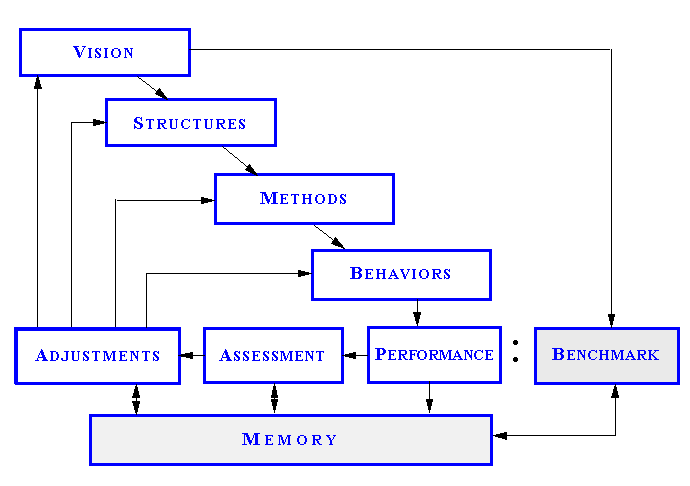
Beliefs |
Notions held dearly, change
by generation, influence decisions and actions
in many, tiny ways every day, and
includes: foundations of culture, ideals,
visions, sense of identity.
|
Executive responsibility,
10-20 year time horizon, very high impact, and
nearly impossible to manage. |
Lead organization
adaptation of a coherent set of beliefs.
Communicate the rationale and vision of
the future. It must be desirable and
feasible. |
|
Structures |
Method expeditors
which are consistent with beliefs and includes:
policies, facilities, infrastructure, equipment,
habit, relationships and targets. |
Management's
responsibility, 2-5 year time horizon,
substantial impact and difficult to manage.
|
Devise, adjust
and promulgate structures in support of
methods and beliefs; must be viewed as
helpful, not hurtful, and desirable.
|
|
Methods |
The procedures
and processes that the business executes
and includes: instructions, recipe's,
and accumulated know-how. |
Supervision's
responsibility, 3 month to 1 year
time horizon. Essential, but stable,
positive impact and not difficult to
manage. |
Train and
refine line workers with particular
attention to start-up. Give feedback
on above and share with below. |
|
Behaviors |
The decisions,
motions and conduct of workers in response
cumulative effects of the above and their
personal capabilities and proclivities.
|
Line worker
responsibility, 1 minute to 1 day time
horizon. The culmination of the above
and requires little management. |
Participate
in and learn about the above, give
feedback and suggestions. |
|
Program
® |
COMPARISON
|
IMPROVEMENT
(gains of 10-20%) |
STEP CHANGE
(gains of 100-200%) |
|
|
|
Executive |
- Authorize benchmarking and data gathering
- Decide if findings warrant step change.
|
- Commit to sustained effort and constancy of purpose
- Support systemic improvement despite short term costs.
|
- Design coherent set of beliefs
- Get concensus at all levels at site
- Finance pilot adequately
- Allow 1 year for results
- Legitimize trial and error.
|
|
Managerial |
- Decide on performance metrics for benchmarking
- Set schedule for data gathering
- Present findings to executives.
|
- Adopt Deming's methods
- Dismantle disabling structures
- Commit to educating
- Set clear, actionable overall goals.
|
- Present contrasting beliefs of others to executives
- Insulate pilot site from "old beliefs"
- Pick basis of measurement
- Encourage trial and error.
|
|
Supervisory |
- Comment on metrics and schedule
- Supervise data gathering
- Decide on delivery medium and format of data
- Check consistency.
|
- Commit to Deming and worker actualization
- Become educated in above
- Make and hear suggestions
- Promote teamwork.
|
- Suggest specific business needs
- become educated in "new ways"
- Hear suggestions
- Allow trial and error.
|
|
Line |
- Gather data
- Make suggestions
- Offer explanations
- Annotate and keep raw data.
|
- Become educated in Deming and SPC
- Work in teams and try technical and social improvement ideas
- Measure, measure, measure.
|
- Commit to "new beliefs"
- Become educated in "new ways"
- Made suggestions
- Try and learn from errors.
|
|
Program
® |
COMPARISON |
IMPROVEMENT
(gains of 10-20%) |
STEP CHANGE
(gains of 100-200%) |
|
Category
¯ |
|
Beliefs |
- Longitudinal performance of competitor
- Productivity of labor and capital
- Cycle time of re-invention / re-engineering.
|
- Productivity of labor and capital
- Standing among competitors.
|
- Philosophy regarding: Customers, Suppliers,
Employees, Partners, Investors and Society
- Views about risks, success, learning, identity.
|
|
Structures |
- Paradigms & beliefs organizing structures
- Performance of system vs. parts.
|
- Alignment of initiatives & direction
- Alignment of personnel policies
- Defecting customers, suppliers, & disaffected employees
- Plant location & layout.
|
- Configuration of suppliers, factory, machines
- Empowerment of supervisors and workers
- Decision making "point of view"
- Clarity of thought.
|
|
Methods |
- Cycle times: Set-up, quality to quality, product variation, ...
- Introduction times: Lags on technology, product, capacity.
|
- Time & motion data & trends
- Defects and warranty work
- Grumbling & suggestions
- Diffusion & adoption of Deming
|
- System thruput & cost
- Trends in quality
- Responisveness to change & variety
- Diffusion & adoption of "new ways"
|
|
Behaviors |
- Availability of tools, supplies, support, education, benefits, ...
- Contributions beyond call of duty
- Conditions & influences at work.
|
- Defects & personal productivity, actual & expected
- Outdated policies, infrastructure & tools
- Ideas for improvement.
|
- Defects & personal productivity, actual & expected
- New policies, infrastructure & tools
- Ideas for improvement
- Amount of education received.
|